Rhinoceros Beetles - Unveiling the Secrets
Imagine a beetle that could flip a car! Believe it or not, these incredible creatures exist – and they're called rhinoceros beetles. With horns like a knight and the strength of a weightlifter, these titans of the insect world are unlike anything you've ever seen.
Get ready to dive into the fascinating world of rhinoceros beetles, where battles for dominance are fought with horns, and the secrets of their strength will leave you astonished.
What are Rhinoceros Beetles?
Rhinoceros beetles are a subfamily of scarab beetles, known for their incredible diversity with over 1500 species. These beetles are part of the family Scarabaeidae, which includes many other fascinating insects like dung beetles and June beetles.
These beetles can range from 4mm to 6 inches in size and are found in various terrestrial habitats worldwide, except for polar regions. They have a diverse diet, with larvae feeding on wood, roots, and decaying material, while adults consume nectar, sap, leaves, and fruit.
Rhinoceros beetles are known for their strength, with males capable of lifting objects up to 850 times their weight.
They produce hissing or squeaking sounds by rubbing their abdomen against their wing covers as a defense mechanism. These beetles have a lifespan of 1-3 years and are nocturnal, with most of their feeding occurring during the larval stage.
The Horned Distinction
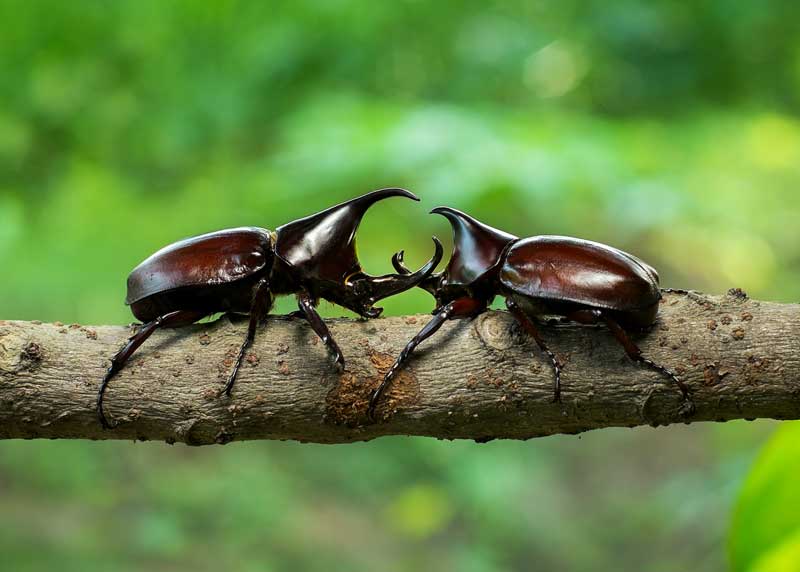
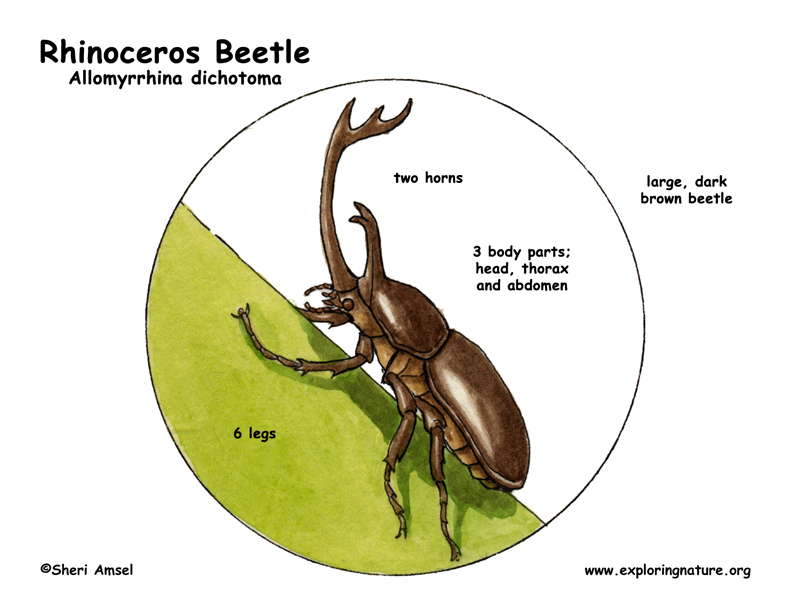
The name "Rhinoceros Beetles" originates from the impressive horns, or tubercles, found on the males of these species. These horns play a crucial role in the mating rituals of these beetles, where males use them to fight for dominance and attract mates. The size and shape of these horns can vary significantly between species, making each one unique and fascinating.
Worldwide Distribution
Rhinoceros beetles are found all over the world, excluding Antarctica. They are a common sight in many regions, including tropical and subtropical areas. Some of the most common regions where they can be found include Southeast Asia, Africa, and parts of North and South America. These beetles thrive in a variety of environments, from forests to grasslands, and are often attracted to sources of light and warmth.
Anatomy of a Rhinoceros Beetle
Rhinoceros beetles, scientifically known as Dynastinae, are a group of beetles recognized for their impressive size and unique physical characteristics.
These beetles are sometimes referred to as Hercules beetles, horn beetles, or unicorn beetles. They are among the largest beetles globally, with some species reaching up to 6 inches in length.
The body of a rhinoceros beetle is covered in a hard exoskeleton made of chitin, which varies in color among species, including red, black, purple, and yellow. Most species have a pair of wings under their shell, although their large size hinders their flying ability.
One of the most distinctive features of rhinoceros beetles is the long horn-like appendages, typically found only on males. These beetles have two horns, one extending upward from the front of the head and another placed at the rear of the thorax pointing forward. Males use these horns for digging and competing with other males during mating seasons .
Beyond the Horns
In addition to their impressive horns, rhinoceros beetles have several other interesting anatomical features:
- Mandibles: These powerful jaws are used for feeding on tree sap, fruit, and other plant matter.
- Legs: The beetles' legs are adapted for digging and climbing, with sharp claws that help them grip onto surfaces.
- Sensory organs: Rhinoceros beetles have compound eyes and antennae that help them navigate their environment and detect potential mates.
Life Cycle of a Rhinoceros Beetle
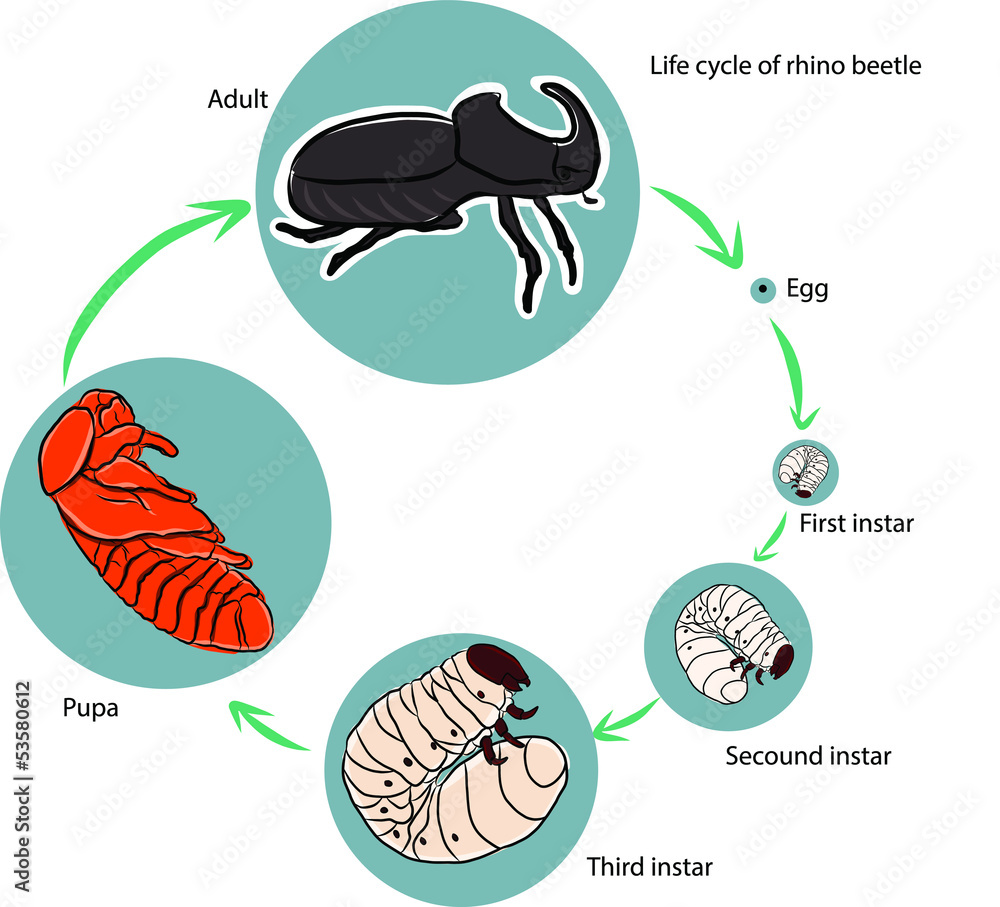
The life cycle of a rhinoceros beetle consists of four main stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult .
Egg Stage
The female beetle lays hundreds of small, oval-shaped white or yellow eggs, usually on leaves or in rotten wood . The eggs hatch after 1.5-2 weeks .Larva Stage
When the eggs hatch, the larvae emerge as C-shaped white grubs . The larval stage includes three substages called instars (L1, L2, L3) . During this stage, the larvae have voracious appetites and feed on decaying plant matter . The larvae molt their exoskeletons 7-10 times as they grow . The larval stage lasts around 4-6 months .Pupa Stage
After the larval stage, the fully grown larvae construct a protective cell and pupate . This is the stage where the greatest change in form takes place, as the larva transforms into the adult beetle shape . The pupal stage lasts around 3 weeks .Adult Stage
After emerging from the pupa, the young adult beetles remain in the breeding site for an additional 3-4 weeks until their exoskeletons harden and their flight muscles and reproductive organs fully develop . They then leave the breeding site, fly to a nearby palm tree, and begin feeding and mating . Adult rhinoceros beetles are herbivorous and feed on fruit, nectar, and sap .The total lifespan of a rhinoceros beetle is typically 1-2 years, with much of this time spent in the larval stage . The larvae are the most destructive life stage, as wood-boring species can damage structures by feeding on the cellulose in timber .
The Strength of Rhinoceros Beetles
Nature's Weightlifters
Rhinoceros beetles are nature's weightlifters, showcasing incredible strength by lifting objects many times their own weight. This remarkable ability sets them apart in the insect world.
The Science Behind the Strength
Their strength stems from a combination of factors. The exoskeleton structure of rhinoceros beetles provides a sturdy framework, while their powerful muscles generate the force needed to lift heavy objects. This structural design allows them to exhibit exceptional strength.
Strength in Numbers
The evolution of such impressive strength in rhinoceros beetles can be attributed to various factors. One key reason is the intense competition for mates. Males with greater strength have a competitive advantage in securing a mate. Additionally, the ability to lift heavy objects aids in resource acquisition, ensuring their survival and reproductive success.
Rhinoceros Beetles and Us: Friends or Foes?
Rhinoceros Beetles and Human Safety
Rhinoceros beetles, despite their intimidating appearance, are actually harmless to humans. They do not possess the ability to sting or bite, making them safe to interact with.
Ecological Benefits
- These beetles play a crucial role in ecosystems by aiding in decomposition processes. They help break down organic matter like dead trees and leaf litter, which in turn contributes to nutrient cycling.
- By recycling nutrients back into the soil, rhinoceros beetles help maintain the health and balance of ecosystems, supporting plant growth and biodiversity.
Cultural Significance
- In various parts of the world, rhinoceros beetles hold cultural significance. They are sometimes kept as pets or admired for their strength, symbolizing power and resilience.
- Additionally, in some cultures, rhinoceros beetles are involved in beetle fighting competitions, where they showcase their strength and agility. Ethical concerns in such activities are addressed through proper care and regulations to ensure the well-being of the beetles.
Conclusion
From their impressive horns to their incredible strength, rhinoceros beetles have captivated our imaginations for centuries. These ecological powerhouses play a vital role in decomposition, ensuring healthy ecosystems around the world https://www.nationalgeographic.org/society/.
However, habitat loss due to deforestation threatens these fascinating creatures. To learn more about the conservation efforts underway to protect rhinoceros beetles, you can visit the websites of organizations like The Entomological Society of America and The Rainforest Trust.