What Do Mosquito Bites Look Like?
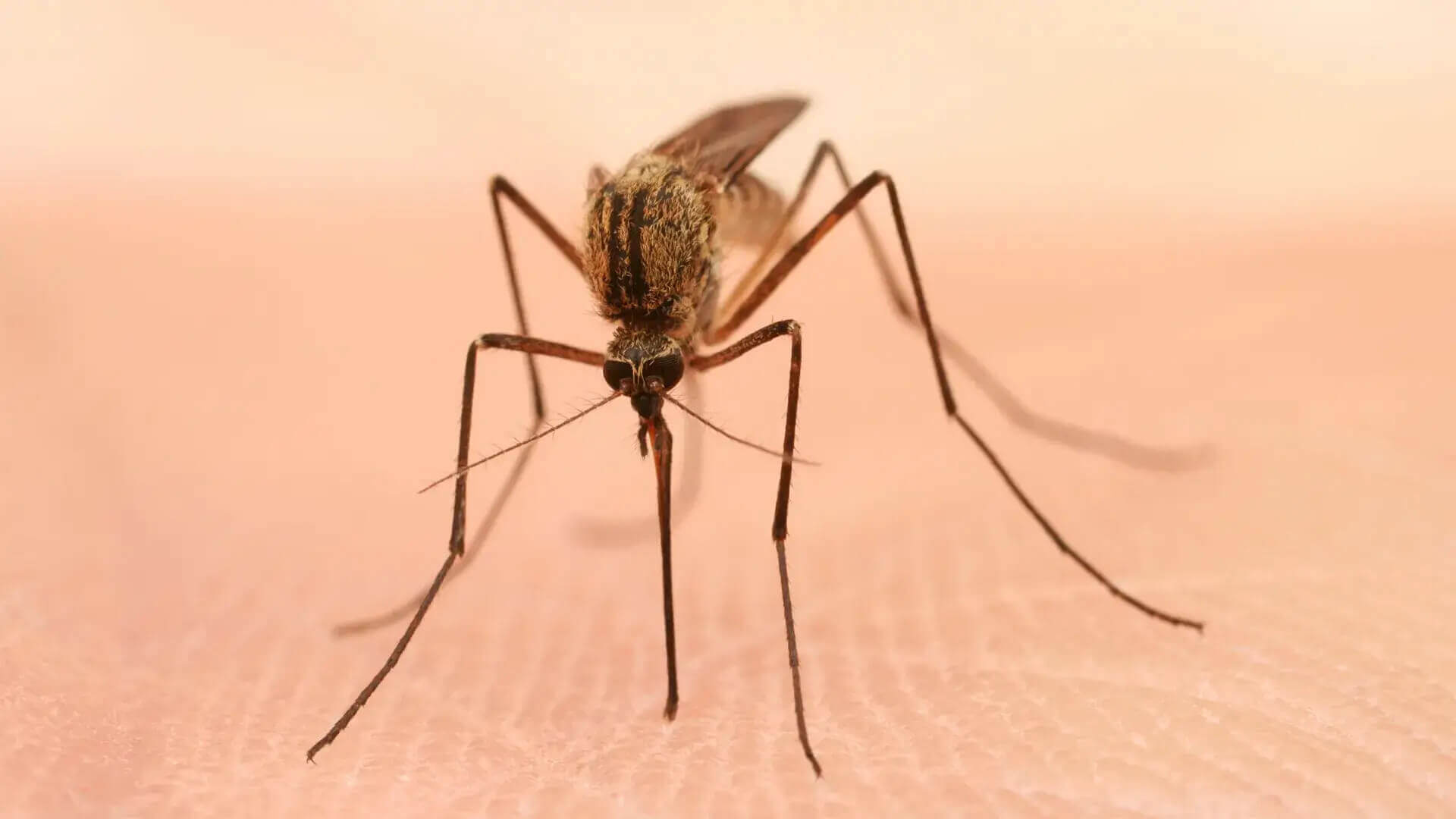
The Anatomy of a Bite
Female mosquitoes employ a fascinating process to obtain a blood meal, involving the use of their specialized mouthpart, the proboscis. This intricate feeding mechanism is both intriguing and essential for their reproductive cycle.
Mosquito Proboscis
- The proboscis is a long, slender mouthpart, resembling a needle, located at the front of the mosquito's head.
- Composed of six stylets, the proboscis includes two mandibles, two maxillae, a hypopharynx, and a labrum. Each element plays a distinct role during feeding.

Biting Process
Piercing the Skin:
- The mosquito uses its mandibles to pierce the skin, creating a pathway for blood extraction.
Saliva Injection:
- Simultaneously, the maxillae release saliva into the punctured blood vessel.
- Mosquito saliva contains anticoagulants and proteins that prevent blood clotting, facilitating efficient feeding.
Blood Extraction:
- With the blood vessel now accessible, the mosquito employs its labrum to draw blood into its digestive system.
- The hypopharynx secretes additional saliva, ensuring a continuous flow of anticoagulants during feeding.
Itchy Reaction
- The introduction of mosquito saliva triggers an immune response in the host.
- Anticoagulants and proteins present in the saliva cause redness, swelling, and itching at the bite site.
- Histamines released by the body to counteract the foreign substances contribute to the characteristic itchiness.
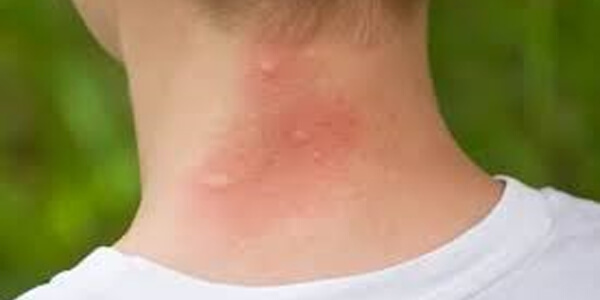
Common Mosquito Bite Appearance
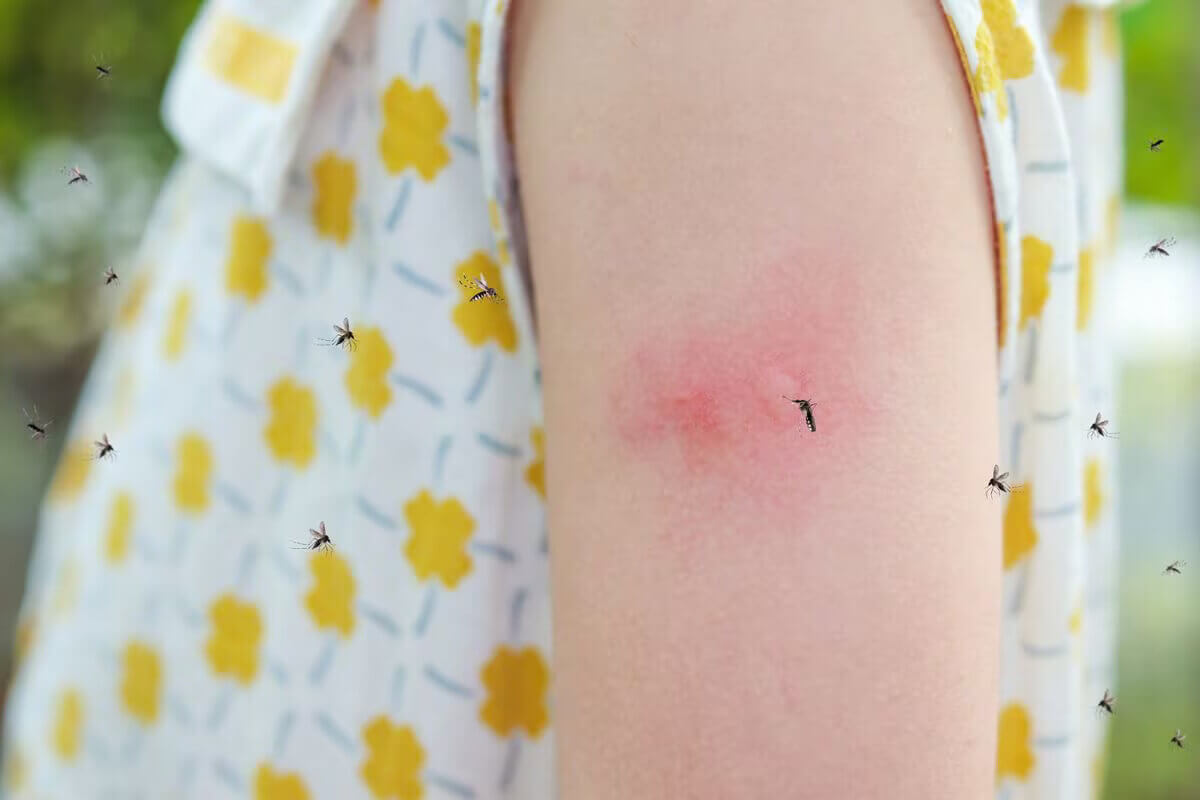
Characteristics of Mosquito Bite:
Small, raised bump (papule): Mosquito bites typically manifest as small, elevated bumps on the skin, known as papules.
Redness and swelling: The affected area often exhibits redness and swelling, contributing to the noticeable appearance of the bite.
Itchy Sensation: One of the hallmark signs is an intense itchiness, causing discomfort to the individual who has been bitten.
Possible Small Red Dot in the Center (Puncture Site): In some cases, a small red dot at the center of the bump may be visible, indicating the mosquito's puncture site.
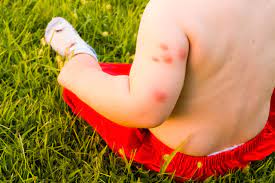
Variations in Mosquito Bite Appearance
Individual Reactions:
- Blisters in Some Individuals:
- Mosquito bites can trigger an allergic reaction in some individuals, leading to the formation of blisters.
- Allergic responses vary, and blisters may not occur in everyone.
Mosquito Species Influence:
Clusters of Bites:
- Different mosquito species have varying feeding behaviors.
- Some species feed in clusters, resulting in multiple bites close together rather than individual bumps.
Bruise-like Discoloration:
- Mosquito saliva contains anticoagulants that can cause mild bruising in some people.
- Older bites may show discoloration resembling a bruise due to the body's response to the saliva.
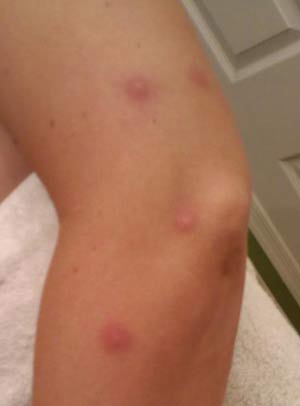
Factors Affecting Mosquito Bite Severity
Mosquito bites can vary in severity, with several factors influencing the outcome. Understanding these factors is crucial for managing symptoms and preventing complications.
Allergies
- Description: Individuals may have allergic reactions to mosquito saliva.
- Impact: Allergic responses can intensify itching and swelling.
- Management: Use antihistamines or consult a healthcare professional for severe reactions.
Scratching
- Description: Scratching mosquito bites exacerbates inflammation.
- Impact: Intense scratching can break the skin, leading to open wounds.
- Consequence: Increases the risk of infection and prolongs healing.
- Prevention: Encourage avoiding scratching to minimize complications.
Infection
- Description: Open wounds from scratching create entry points for bacteria.
- Impact: Infection can result in redness, swelling, and systemic symptoms.
- Prevention: Clean bites with mild soap, apply antiseptic, and avoid scratching.
Importance of Avoiding Scratching
- Rationale: Scratching increases the risk of complications.
- Preventive Measures: Use anti-itch creams, cold compresses, or wear protective clothing.
- Avoiding scratching is crucial to prevent infections and expedite healing. Scratching can introduce bacteria, leading to complications. By refraining from scratching, one enhances the healing process and reduces the risk of infections.
Tips for Soothing Itchy Mosquito Bites
1. Cold Compress Application
Applying a cold compress to mosquito bites can help alleviate itching and reduce inflammation. This simple remedy constricts blood vessels, providing immediate relief.
2. Calamine Lotion or Anti-Itch Cream
Calamine lotion and anti-itch creams are effective in soothing mosquito bites. They contain ingredients like zinc oxide or hydrocortisone, which help reduce itching and inflammation.
3. Baking Soda Paste
A baking soda paste can be made by mixing baking soda with water to create a soothing solution. Applying this paste to mosquito bites can provide relief by reducing irritation and itching.
4. Avoiding Harsh Soaps and Hot Water
Using harsh soaps and hot water can exacerbate mosquito bites by irritating the skin further. Opt for mild, fragrance-free soaps and lukewarm water to minimize discomfort.
Mosquito Bite Prevention Strategies
1. Using Insect Repellent
- Choose a repellent with an effective active ingredient (e.g., DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus).
- Apply the repellent to exposed skin and clothing before heading to mosquito-prone areas.
- Reapply as directed on the product label, especially if sweating or spending an extended time outdoors.
2. Wearing Protective Clothing in Mosquito-Prone Areas
- Opt for long sleeves, pants, and socks to minimize exposed skin.
- Use light-colored clothing, as mosquitoes are attracted to dark colors.
- Consider clothing treated with permethrin for added protection.
3. Eliminating Breeding Grounds Around Your Home
- Remove stagnant water from containers, gutters, and flowerpots where mosquitoes breed.
- Keep outdoor areas tidy to reduce hiding spots for mosquitoes.
- Use mosquito larvicides in standing water to prevent the development of larvae.
By following these mosquito bite prevention strategies, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of mosquito-borne illnesses and ensure a safer outdoor experience.
Mosquitoes and Their Bites: Interesting Facts
1. Diversity of Mosquito Species
- Mosquitoes belong to the order Diptera, which includes flies.
- There are over 3,500 species of mosquitoes worldwide.
- Only female mosquitoes bite, as they require blood for egg development.
2. Attracted to Carbon Dioxide
- Mosquitoes are highly attracted to carbon dioxide, a gas we exhale.
- The carbon dioxide emitted during breathing helps mosquitoes locate their hosts.
3. Preference for Blood Types
- Mosquitoes may have preferences for certain blood types.
- People with Type O blood are believed to be more attractive to mosquitoes.
4. Feeding Behavior
- Mosquitoes primarily feed on nectar and plant juices.
- Female mosquitoes use the nutrients from blood to develop their eggs.
5. Malaria Transmission
- Mosquitoes are known vectors for diseases such as malaria.
- The female Anopheles mosquito is responsible for transmitting the Plasmodium parasite causing malaria.
6. Itchiness from Bites
- Mosquito bites cause itching due to proteins in their saliva.
- Scratching the bite can lead to skin irritation and potential infection.
7. Mosquito Lifespan
- The lifespan of a mosquito varies by species.
- On average, mosquitoes live for about 2 weeks to a month.
8. Mosquito Repellents
- Various natural and chemical repellents help protect against mosquito bites.
- DEET, picaridin, and citronella are common ingredients in mosquito repellent products.
9. Mosquitoes and Water Breeding
- Mosquitoes lay their eggs in standing water.
- Eliminating standing water helps control mosquito populations.
10. Worldwide Distribution
- Mosquitoes are found on every continent except Antarctica.
- Different species thrive in various climates and environments.
Conclusion
Understanding the appearance of mosquito bites and knowing how to treat them is crucial for relief and preventing complications. Recognizing features like redness and swelling enables prompt action, utilizing remedies such as anti-itch creams and preventive measures like insect repellent. Turning annoyance into manageable inconvenience, staying informed and proactive is key.
